ADMINISTRATION OF FISHING
Fishing is administrated through quotas and licenses regulating the total allowable catch for Greenlandic waters. Licences are used to regulate access to fishing. The system of quotas and licenses is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
The System of TAC, Quotas, and Licences
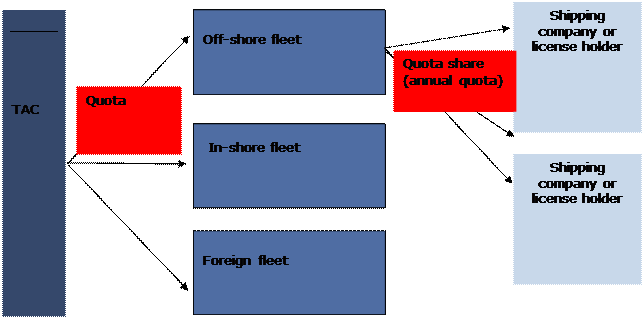
Total Allowable Catch, TAC
The Government of Greenland sets an annual total allowable catch (TAC) of the fish stock of the territorial waters of Greenland. The decision is made based on the biological advice provided by Pinngortitaleriffik (Greenland Institute of Natural Resources) in cooperation with several international fisheries organizations, see International Fishery Agreements and Organizations.
The Fisheries Council consisting among others of representatives from the Association for Coastal Fishermen and Hunters in Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaani Aalisartut Piniartullu Kattuffiat, KNAPK) and the employers' associations (GA and NUSUKA) are consulted before the TAC is set.
The total allowable catch is distributed in the form of quotas to individual units of the fleet. A distinction is made between coastal fishing and ocean fishing.
Coastal fishing takes place from small vessels below 75 GRT/120 GT within the limit of three nautical miles.
Ocean fishing takes place from vessels over 75 GRT /120 GT outside the limit of three nautical miles (off-shore). Quotas are also granted to other nations, see International Fishery Agreements and Organizations.
The seagoing fleet is granted 57 per cent of the total shrimp quota for West Greenland while the remaining 43 per cent are allocated to the in-shore fleet. The distribution of quotas for other species is determined by the Greenlandic government.
Figure 2
Total Allowable Catch in Greenlandic Waters for Select Species
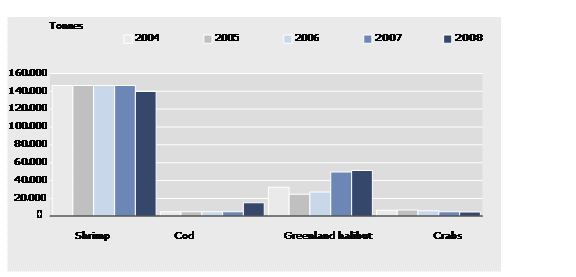
Note: The figures concern the TAC's as fixed by the government.
Source: 'Statement to the Parliament on TAC and Quotas' and departmental orders on quotas
The TAC for shrimp is set for West and for East Greenland.
The total amount of shrimp and other selected species is shown in Figure 2.
The annual allowable catch of cod is set for Greenland as a whole.
The TAC for off-shore fishing for Greenland halibut in West Greenlandic waters is determined for the fish stocks in the Davis Strait and the Baffin Bay, respectively.
Fishing for crab only takes place in West Greenland. As shown in Figure 2, the permitted catch of crabs declined from 27.000 tonnes in 2002 to 4.700 tonnes in 2008.
Table 1 provides more details on the TAC for fish in Greenlandic waters. Table 2 shows the evolution of the Greenlandic quota in Greenland for in-shore and off-shore fishing respectively.
Licenses
The right to fish is regulated through licensing. In Greenlandic fishing, a license was mandatory in 2008 for off-shore fishing for shrimp, halibut, crab, cod, redfish, halibut, capelin, and grenadier.
In in-shore fishing, a license was mandatory in 2008 for fishing for shrimp, halibut, crab, salmon, lumpfish, and scallops.
A distinction is made between three types of licenses; temporary licenses with or without an upper limit for the allowable catch and permanent licenses with an upper limit for the allowable catch.
Permanent licenses with a maximum allowable catch are used for shrimp. The individual shipping companies or persons have the license to a certain share of the quota of their fleet segment. After setting the TAC, the government notifies the license holders which annual quota the individual licenses represent.
Licenses can be traded between ship owners and individual persons. In off-shore shrimp fishing, one single company or person can at the most hold one third of the total shrimp quota. In the coastal shrimp fishing, the maximum share is 10 per cent of the total shrimp quota.
Temporary licenses with an upper limit for the allowable catch are used in the ocean-going fishing for halibut, cod, redfish, halibut, capelin, and grenadier. In coastal fishing, this type license is used for fishing for scallops. Licences are issued for one year and include information on the yearly quota for each individual vessel.
Temporary licenses without an upper limit for the allowable catch are used in the coastal fishing for halibut and crab in which all Greenlandic vessels share the quota.
Fishing Licence Control of Greenland (GFLK)
The Fishing Licence Control of Greenland (GFLK) is a section under the Agency for Fishing, Catching, and Agriculture. The primary tasks of GFLK are to check logs and monitor the movements and activity in Greenlandic waters of trawlers via satellite. Moreover, GFLK positions observers on foreign and Greenlandic fishing vessels, primarily shrimp trawlers. The actual fishing inspection is conducted by the Island Command Greenland (GLK), carrying out inspections of vessels, catch and fishing equipment at sea, cf. this section on defence.
Links
Read more about the Greenland Institute of Natural Resources and the biological advice of the institute at www.natur.gl.
Read more about TAC's at http://ec.europa.eu/fisheries.
Read more about KNAPK at www.knapk.gl.
Read more about GA at www.ga.gl.
Read more about fishing control at www.nanoq.gl.
Read more about the Island Command Greenland at www.forsvaret.dk.